Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
"ISIL", "Isil", and "ISIS" redirect here. For other uses, see ISIL (disambiguation) and Isis (disambiguation).
Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant
الدولة الإسلامية في العراق والشام (Arabic) ad-Dawlah al-Islāmīyah fil 'Irāq wa ash-Shām(transliteration)
Participant in the Iraq War (2003–2011) andInsurgency (2011–present), the Syrian Civil Warand its spillover, the 2014 Libyan Civil War, and the Sinai insurgency.
Primary target of the 2014 military intervention against ISIL, the intervention in Iraq and Syria, as well as the Iranian and Turkish interventions, and the Global War on Terrorism | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
| Motto: باقية وتتمدد "Bāqiyah wa-Tatamaddad" "Remaining and Expanding" [1] | ||||||
| Anthem: أمتي قد لاح فجر Ummatī, qad lāha fajrun "My Nation, Dawn Has Appeared"[2][3] | ||||||
|
Military situation as of 20 December 2014, in Iraq and Syria.
Controlled by the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant
Controlled by al-Nusra
Controlled by other Syrian rebels
Controlled by Syrian government
Controlled by Iraqi government
Controlled by Syrian Kurds
Controlled by Iraqi Kurds
Note: Syria and Iraq contain large desert areas with limited population. These areas are mapped as under the control of forces holding roads and towns within them. | ||||||
| Administrative center | Ar-Raqqah, Syria (de facto)[5][6] 36°34′N 43°13′E | |||||
| Largest city | Mosul, Iraq | |||||
| Ideologies | Sunni Islamism Anti-Shiaism[7] Salafist Jihadism Takfirism Wahhabism | |||||
| Type | Rebel group controlling territory | |||||
| Military strength & operation areas | Inside Iraq and Syria 200,000[11] (Kurdish claim) 20,000–31,000 (CIA estimate) Outside Iraq and Syria 19,500–31,000 (SeeMilitary of ISIL for more-detailed estimates.) | |||||
| Leaders | ||||||
| - | Leader | Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi[12] | ||||
| - | Field commander | Abu Omar al-Shishani[13][14][15] | ||||
| - | Spokesman | Abu Muhammad al-Adnani[16][17] | ||||
| Establishment | ||||||
| - | Formation (as Jamāʻat al-Tawḥīd wa-al-Jihād) | 1999[18] | ||||
| - | Joined al-Qaeda | October 2004 | ||||
| - | Declaration of an Islamic state in Iraq | 13 October 2006 | ||||
| - | Claim of territory in theLevant | 8 April 2013 | ||||
| - | Separated from al-Qaeda[19][20] | 3 February 2014[21] | ||||
| - | Declaration of "Caliphate" | 29 June 2014 | ||||
| - | Claim of territory in Libya,Egypt, Algeria, Saudi Arabia, and Yemen | 13 November 2014 | ||||
| Area | ||||||
| - | Estimate only of controlled areas | 32,133 km2[22] 12,407 sq mi | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | 12 June 2014 The New York Times estimate | 8,000,000 in controlled areas[23] | ||||
| Time zone | Eastern European Timeand Arabia Standard Time (UTC+2 and +3) | |||||
The Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL /ˈaɪsəl/),(Arabic: الدولة الاسلامية في العراق والشام) is also translated as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria or ash-Sham referring to Greater Syria (ISIS /ˈaɪsɪs/),) ad-Dawlah al-Islāmīyah fīl-ʻIrāq wa ash-Shām) The group is also known by the Arabic acronym Daʿish or DAESH (Arabic: داعشDāʻish). Since June 2014 it calls itself the Islamic State (IS), a name widely rejected by non-members. ISIL is aSunni extremist, jihadist rebel group based in Iraq and Syria, where it controls territory. It also operates in eastern Libya, the Sinai Peninsula of Egypt, and other areas of the Middle East,[24] North Africa, South Asia,[25]and Southeast Asia.[26]
The United Nations has held ISIL responsible for human rights abuses and war crimes, and Amnesty International has reported ethnic cleansing by the group on a "historic scale". The group has been designatedas a terrorist organization by the United Nations, the European Union, the United Kingdom, the United States, Australia, Indonesia, Canada, Turkey, Saudi Arabia, India, the UAE, and Egypt. Over 60 countries are directly or indirectly waging war against ISIL.
The group originated as Jama'at al-Tawhid wal-Jihad in 1999, which was renamed Tanzim Qaidat al-Jihad fi Bilad al-Rafidayn—commonly known as al-Qaeda in Iraq (AQI)—when the group pledged allegiance to al-Qaeda in 2004. Following the 2003 invasion of Iraq, AQI took part in the Iraqi insurgency. In 2006, it joined other Sunni insurgent groups to form the Mujahideen Shura Council, which shortly afterwards proclaimed the formation of an Islamic state, naming it the Islamic State of Iraq (ISI). The ISI gained a significant presence in Al Anbar, Nineveh, Kirkuk and other areas, but around 2008, its violent methods, including suicide attacks on civilian targets and the widespread killing of prisoners, led to a backlash from Sunni Iraqis and other insurgent groups.[a]
The group grew significantly under the leadership of Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, and after entering the Syrian Civil War, it established a large presence in Sunni-majority areas of Syria within the governorates of Ar-Raqqah,Idlib, Deir ez-Zor and Aleppo.[27] Having expanded into Syria, the group changed its name in April 2013 to the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant, when al-Baghdadi announced its merger with the Syrian-based group al-Nusra Front. The group remained closely linked to al-Qaeda until February 2014, when after an eight-month power struggle, al-Qaeda cut all ties with ISIL, citing its failure to consult and "notorious intransigence".[21][28]
On 29 June 2014, the group proclaimed a worldwide caliphate,[29][30] Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi—known by his supporters as Amir al-Mu'minin, Caliph Ibrahim—was named its caliph, and the group was renamed the Islamic State.[31] As caliphate it claims religious, political and military authority over all Muslims worldwide.[32] This is while ISIL's actions have been widely criticized around the world, with many Islamic communities judging the group to be unrepresentative of Islam. One of ISIL's goals has been to establish a radical Sunni Islamist state in Iraq and the Levant region, which covers Syria, Jordan, Israel, Palestine, Lebanon, Cyprus, and Hatay province in southern Turkey.[33] Groups controlling territory in Sinai, eastern Libya, and Pakistan have been absorbed by ISIL.
ISIL is widely known for its violent propaganda, which includes Internet videos of beheadings—see 2014 ISIL beheading incidents.
Contents
[hide]- 1 History
- 2 Group goals, structure and characteristics
- 3 Designation as a terrorist organization
- 4 Human rights abuse and war crime findings
- 5 Criticism
- 6 Analysis
- 7 Countries and groups at war with ISIL
- 8 Supporters
- 9 Military and resources
- 10 Timeline of recent events
- 11 See also
- 12 Notes
- 13 References
- 14 Bibliography
- 15 External links
History
Part of a series on the
|
|---|
| Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant History |
 Black Standard variant adopted by ISI |
Jama'at al-Tawhid wal-Jihad (1999–2004)
Mujahideen Shura Council (2006)
Islamic State of Iraq (2006–13)
Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (2013–14)
Self-proclaimed as the Islamic State (2014–present) |
| By topic |
See also: Timeline of Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant events, Islamic State of Iraq § Timeline, Syrian Civil War § Course of events and Terrorist incidents in Iraq in 2014
Outline of history – with links to content below
- As Jama'at al-Tawhid wal-Jihad (Organization of Monotheism and Jihad) (1999–2004)
- As Tanzim Qaidat al-Jihad fi Bilad al-Rafidayn (al-Qaeda in Iraq) (2004–2006)
- As Mujahideen Shura Council (2006)
- As Islamic State of Iraq (2006–2013)
- As Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (2013–2014)
- As Islamic State (2014–present)
Names
The group has had various names since it was established.[34]
- The group was founded in 1999 by Abu Musab al-Zarqawi under the name Jamāʻat al-Tawḥīd wa-al-Jihād, "The Organization of Monotheism and Jihad" (JTJ).[18]
- In October 2004, al-Zarqawi swore loyalty to Osama bin Laden and changed the group's name toTanẓīm Qāʻidat al-Jihād fī Bilād al-Rāfidayn, "The Organization of Jihad's Base in Mesopotamia", commonly known as al-Qaeda in Iraq. (AQI).[34][35] Although the group has never called itself al-Qaeda in Iraq, this has been its informal name over the years.[36]
- In January 2006, AQI merged with several other Iraqi insurgent groups to form the Mujahideen Shura Council.[37] Al-Zarqawi was killed in June 2006.
- On 12 October 2006, the Mujahideen Shura Council merged with several more insurgent factions, and on 13 October the establishment of the Dawlat al-ʻIraq al-Islāmīyah, Islamic State of Iraq (ISI) was announced.[34][38] The leaders of this group were Abu Abdullah al-Rashid al-Baghdadi and Abu Ayyub al-Masri.[39] After they were killed in a US–Iraqi operation in April 2010, Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi became the new leader of the group.
- On 8 April 2013, having expanded into Syria, the group adopted the name Islamic State of Iraq and al-Sham, which more fully translates as Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant or Islamic State of Iraq and Syria.[40][41][42] These names are translations of the Arabic name al-Dawlah al-Islāmīyah fī al-ʻIrāq wa-al-Shām,[43][44] al-Shām being a description of the Levant or Greater Syria.[45] The translated names are commonly abbreviated as ISIL or ISIS.
- The name Daʿish is often used by ISIL's Arabic-speaking detractors. It is based on the Arabic letters dāl, alif, ʻayn, and shīn, which form the acronym (داعش) of ISIL's Arabic name al-Dawlah al-Islamīyah fī al-ʻIrāq wa-al-Shām.[46][47] There are many different spellings of this acronym. ISIL considers the name Da'ish derogatory—it is thought to translate as “to tread underfoot, trample down, crush”[48]—and reportedly uses flogging as a punishment for those who use the name in ISIL-controlled areas.[49][50]
- On 14 May 2014, the United States Department of State announced its decision to use "Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant" (ISIL) as the group's primary name.[46] Which of these acronyms should be used to designate the group, ISIL or ISIS, has been debated,[44][45] with The Washington Post concluding that the distinction between the two "is not so great"."[45]
- On 29 June 2014, the group renamed itself the Islamic State (IS) and declared a "caliphate".[31][51][52][b]
Foundation of the group (1999–2006)
Main articles: Jama'at al-Tawhid wal-Jihad, Tanzim Qaidat al-Jihad fi Bilad al-Rafidayn and Mujahideen Shura Council (Iraq)
Following the 2003 invasion of Iraq, the Jordanian Salafi Jihadist Abu Musab al-Zarqawi and his militant group Jama'at al-Tawhid wal-Jihad, founded in 1999, achieved notoriety in the early stages of the Iraq insurgency, by not only carrying out attacks on coalition forces but conducting suicide attacks on civilian targets andbeheading hostages.[18][54]
Al-Zarqawi's group grew in strength and attracted more fighters, and in October 2004 it officially pledged allegiance to Osama bin Laden's al-Qaeda network, changing its name to Tanzim Qaidat al-Jihad fi Bilad al-Rafidayn (تنظيم قاعدة الجهاد في بلاد الرافدين, "Organization of Jihad's Base in Mesopotamia"), also known as Al-Qaeda in Iraq (AQI).[19][55][56] Attacks by the group on civilians, the Iraqi Government and security forces continued to increase over the next two years. (See list of major resistance attacks in Iraq.)[57] In a letter to al-Zarqawi in July 2005, al-Qaeda's deputy leader Ayman al-Zawahiri outlined a four-stage plan to expand the Iraq War, which included expelling US forces from Iraq, establishing an Islamic authority, as caliphate, spreading the conflict to Iraq's secular neighbors, and engaging in the Arab–Israeli conflict.[58]
In January 2006, AQI merged with several smaller Iraqi insurgent groups under an umbrella organization called theMujahideen Shura Council (MSC). This was claimed by Brian Fishman in the Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science to be little more than a media exercise and an attempt to give the group a more Iraqi flavour and perhaps to distance al-Qaeda from some of al-Zarqawi's tactical errors, notably the 2005 bombings by AQI of three hotels in Amman.[59] On 7 June, al-Zarqawi was killed in a US airstrike and was succeeded as leader of the group by the Egyptian militant Abu Ayyub al-Masri.[60][61]
On 12 October 2006, the Mujahideen Shura Council joined four more insurgent factions and the representatives of a number of Iraqi Arab tribes, and together they swore the traditional Arab oath of allegiance known as Ḥilf al-Muṭayyabīn ("Oath of the Scented Ones").[c][62][63] During the ceremony, the participants swore to free Iraq's Sunnis from what they described as Shia and foreign oppression, and to further the name of Allah and restore Islam to glory.[d][62]
On 13 October 2006, the Mujahideen Shura Council declared the establishment of the Islamic State of Iraq (ISI), comprising Iraq's six mostly Sunni Arab governorates, with Abu Omar al-Baghdadi being announced as its Emir.[38][57] Al-Masri was given the title of Minister of War within the ISI's ten-member cabinet.[64]The declaration of statehood was met with hostile criticism, not only from ISI's jihadist rivals in Iraq, but from leading jihadist ideologues outside the country.[65]
As Islamic State of Iraq (2006–2013)
Main article: Islamic State of Iraq
According to a study compiled by US intelligence agencies in early 2007, the ISI—also known as AQI—planned to seize power in the central and western areas of the country and turn it into a Sunni Islamic state.[66] The group built in strength and at its height enjoyed a significant presence in the Iraqi governorates of Al Anbar, Nineveh, Kirkuk, most of Salah ad Din, parts ofBabil, Diyala and Baghdad, and claimed Baqubah as a capital city.[67][68][69][70]
However, by late 2007, violent and indiscriminate attacks directed by rogue AQI elements against Iraqi civilians had severely damaged the group's image and caused a loss of support among the population, thus isolating it. In a major blow to AQI, many former Sunni militants who had previously fought alongside the group started to work with the US armed forces. The US troops surge supplied the military with more manpower for operations targeting the group, resulting in dozens of high-level AQI members being captured or killed.[71]
al-Qaeda seemed to have lost its foothold in Iraq and appeared to be severely crippled.[72] During 2008, a series of US and Iraqi offensives managed to drive out the AQI-aligned insurgents from their former safe havens, such as the Diyala and Al Anbar governorates and the embattled capital of Baghdad, to the area of the northern city of Mosul, the latest of the Iraq War's major battlegrounds.[73] By 2008, the ISI was describing itself as being in a state of "extraordinary crisis".[74] Its violent attempts to govern its territory led to a backlash from Sunni Iraqis and other insurgent groups and a temporary decline in the group, which was attributable to a number of factors,[75] notably the Anbar Awakening.
In late 2009, the commander of the US forces in Iraq, General Ray Odierno, stated that the ISI "has transformed significantly in the last two years. What once was dominated by foreign individuals has now become more and more dominated by Iraqi citizens".[76] On 18 April 2010, the ISI's two top leaders, Abu Ayyub al-Masri andAbu Omar al-Baghdadi, were killed in a joint US-Iraqi raid near Tikrit.[77] In a press conference in June 2010, General Odierno reported that 80% of the ISI's top 42 leaders, including recruiters and financiers, had been killed or captured, with only eight remaining at large. He said that they had been cut off from al-Qaeda's leadership in Pakistan, and that improved intelligence had enabled the successful mission in April that led to the killing of al-Masri and al-Baghdadi; in addition, the number of attacks and casualty figures in Iraq for the first five months of 2010 were the lowest since 2003.[78][79][80]
On 16 May 2010, Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi was appointed the new leader of the Islamic State of Iraq.[81][82] Al-Baghdadi replenished the group's leadership, many of whom had been killed or captured, by appointing former Ba'athist military and intelligence officers who had served during the Saddam Hussein regime. These men, nearly all of whom had spent time imprisoned by the US military, came to make up about one-third of Baghdadi's top 25 commanders. One of them was a former Colonel, Samir al-Khlifawi, also known as Haji Bakr, who became the overall military commander in charge of overseeing the group's operations.[83][84]
In July 2012, al-Baghdadi released an audio statement online announcing that the group was returning to the former strongholds from which US troops and theirSunni allies had driven them prior to the withdrawal of US troops.[85] He also declared the start of a new offensive in Iraq called Breaking the Walls, which was aimed at freeing members of the group held in Iraqi prisons.[85] Violence in Iraq began to escalate that month, and by July 2013, monthly fatalities had exceeded 1,000 for the first time since April 2008.[86] The Breaking the Walls campaign culminated in July 2013, with the group carrying out simultaneous raids on Taji and Abu Ghraib prison, freeing more than 500 prisoners, many of them veterans of the Iraqi insurgency.[86][87]
Syrian Civil War (2011–present)
In March 2011, protests began in Syria against the government of Bashar al-Assad. In the following months, violence between demonstrators and security forces led to a gradual militarisation of the conflict.[88] In August 2011, Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi began sending Syrian and Iraqi ISI members experienced in guerilla warfare across the border into Syria in order to establish an organization inside the country. Led by a Syrian known as Abu Muhammad al-Jawlani, this group began to recruit fighters and establish cells throughout the country.[89][90] On 23 January 2012, the group announced its formation as Jabhat al-Nusra li Ahl as-Sham—Jabhat al-Nusra—more commonly known as al-Nusra Front. Al-Nusra grew rapidly into a capable fighting force, with popular support among Syrians opposed to the Assad regime.[89]
As Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (2013–2014)
On 8 April 2013, al-Baghdadi released an audio statement in which he announced that the al-Nusra Front had been established, financed, and supported by the Islamic State of Iraq,[91] and that the two groups were merging under the name "Islamic State of Iraq and Al-Sham".[40] Al-Jawlani issued a statement denying the merger, and complaining that neither he nor anyone else in al-Nusra's leadership had been consulted about it.[92] In June 2013, Al Jazeera reported that it had obtained a letter written by al-Qaeda's leader Ayman al-Zawahiri, addressed to both leaders, in which he ruled against the merger, and appointed an emissary to oversee relations between them to put an end to tensions.[93] In the same month, al-Baghdadi released an audio message rejecting al-Zawahiri's ruling and declaring that the merger was going ahead.[94] In October 2013, al-Zawahiri ordered the disbanding of ISIL, putting al-Nusra Front in charge of jihadist efforts in Syria,[95] but al-Baghdadi contested al-Zawahiri's ruling on the basis of Islamic jurisprudence,[94] and his group continued to operate in Syria. In February 2014, after an eight-month power struggle, al-Qaeda disavowed any relations with ISIL.[28]
According to journalist Sarah Birke, there are "significant differences" between the al-Nusra Front and ISIL. While al-Nusra actively calls for the overthrow of the Assad government, ISIL "tends to be more focused on establishing its own rule on conquered territory". ISIL is "far more ruthless" in building an Islamic state, "carrying out sectarian attacks and imposing sharia law immediately". While al-Nusra has a "large contingent of foreign fighters", it is seen as a home-grown group by many Syrians; by contrast, ISIL fighters have been described as "foreign 'occupiers'" by many Syrian refugees.[96] It has a strong presence in central and northern Syria, where it has instituted sharia in a number of towns.[96] The group reportedly controlled the four border towns of Atmeh, al-Bab, Azaz and Jarablus, allowing it to control the entrance and exit from Syria into Turkey.[96] Foreign fighters in Syria include Russian-speaking jihadists who were part of Jaish al-Muhajireen wal-Ansar(JMA).[97] In November 2013, the JMA's Chechen leader Abu Omar al-Shishani swore an oath of allegiance to al-Baghdadi;[98] the group then split between those who followed al-Shishani in joining ISIL and those who continued to operate independently in the JMA under new leadership.[99]
In January 2014, rebels affiliated with the Islamic Front and the US-trained Free Syrian Army[100] launched an offensive against ISIL militants in and around the city ofAleppo in Syria.[101][102] In May 2014, Ayman al-Zawahiri ordered al-Nusra Front to stop its attacks on its rival, ISIL.[103] In June 2014, after continued fighting between the two groups, al-Nusra's branch in the Syrian town of Al-Bukamal pledged allegiance to ISIL.[104][105] In mid-June 2014, ISIL captured the Trabil crossing on the Jordan–Iraq border,[106] the only border crossing between the two countries.[107] ISIL has received some public support in Jordan, albeit limited, partly owing to state repression there,[108] but ISIL has undertaken a recruitment drive in Saudi Arabia,[109] where tribes in the north are linked to those in western Iraq and eastern Syria.[110]
As so-called Islamic State (June 2014–present)
See also: 2014 ISIL beheading incidents, American-led intervention in Syria, 2014 American-led intervention in Iraq, 2014 Iranian-led intervention in Iraq, 2014 military intervention against the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant, Northern Iraq offensive (June 2014) and Turkish involvement in the 2014 military intervention against ISIL
On 29 June 2014, the group proclaimed a worldwide caliphate,[29] Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi—known by his supporters as Amir al-Mu'minin, Caliph Ibrahim—was named its caliph, and the group renamed itself the "Islamic State".[31] As caliphate, it claims religious, political and military authority over all Muslims worldwide.[30][32] In June and July 2014, Jordan and Saudi Arabia moved troops to their borders with Iraq, after Iraq lost control of, or withdrew from, strategic crossing points that had then come under the control of ISIL or tribes that supported ISIL.[107][111] There was speculation that Iraqi Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki had ordered a withdrawal of troops from the Iraq–Saudi crossings in order "to increase pressure on Saudi Arabia and bring the threat of Isis over-running its borders as well".[110]
In July 2014, ISIL recruited more than 6,300 fighters, according to the Syrian Observatory for Human Rights, some of whom were thought to have previously fought for the Free Syrian Army.[112] On 3 August 2014, ISIL captured the towns of Zumar, Sinjar, and Wana in northern Iraq.[113] The need for food and water for thousands of Yazidis, who fled up a mountain out of fear of approaching hostile ISIL militants, and the threat of genocide to Yazidis and others as announced by ISIL, in addition to protecting Americans in Iraq and supporting Iraq in its fight against the group, were reasons for the US to launch a humanitarian mission on 7 August 2014, to aid the Yazidis stranded on Mount Sinjar[114] and to start an aerial bombing campaign in Iraq on 8 August.
On 11 October 2014, ISIL dispatched 10,000 militants from Syria and Mosul to capture the Iraqi capital city of Baghdad,[115] and Iraqi Army forces and Anbar tribesmen threatened to abandon their weapons if the US did not send in ground troops to halt ISIL's advance.[116] On 13 October, ISIL fighters advanced to within 25 kilometers—15.5 miles—of Baghdad Airport.[117]
At the end of October 2014, 800 radical militants in control of the Libyan city of Derna pledged their allegiance to Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, thus making Derna the first city outside Syria and Iraq to be a part of the so-called "Islamic State caliphate".[118] On 2 November 2014, according to the Associated Press, in response to the coalition airstrikes, representatives from Ahrar ash-Sham attended a significant meeting with al-Nusra Front, the Khorasan Group, ISIL and Jund al-Aqsa, which sought to unite these hard-line groups against the coalition and moderate Syrian rebel groups.[119] On 10 November 2014, a major faction of the Egyptian militant group Ansar Bait al-Maqdis also pledged its allegiance to ISIL.[120]
Group goals, structure and characteristics
Goals and territorial ambitions
Main article: ISIL territorial claims
Since 2004, the group's goal has been the foundation of an Islamic state in Iraq and the Levant.[121][122] Specifically, ISIL has sought to establish itself as a caliphate, an Islamic state led by a group of religious authorities under a supreme leader—caliph—who is believed to be the successor to Muhammad.[123] In June 2014, ISIL published a document in which it claimed to have traced the lineage of its leader Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi back to Muhammad,[123] and upon proclaiming a new caliphate on 29 June, the group appointed al-Baghdadi as its caliph. As caliph, he demands the allegiance of all devout Muslims worldwide according to Islamic jurisprudence (fiqh).[124]
When the caliphate was announced, ISIL stated: "The legality of all emirates, groups, states and organizations becomes null by the expansion of the khilafah's [caliphate's] authority and arrival of its troops to their areas".[123] This was a rejection of the political divisions in the Middle East that were established by Western powers during World War I in the Sykes–Picot Agreement.[125][126][127]
In Iraq and Syria, ISIL uses many of the existing Governorate boundaries to subdivide its claimed territory; it calls these divisions wilayah.[128] After a series of expansions, as of November 2014, it claims provinces and controls territory in Iraq,Syria, Sinai, and eastern Libya. It also claims provinces and has members in Algeria, Saudi Arabia, Yemen but does not control territory in these areas.
Leadership and governance
Further information: List of Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant members
The group is headed and run by Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, with a cabinet of advisers. There are two deputy leaders, Abu Muslim al-Turkmani(KIA) for Iraq and Abu Ali al-Anbari for Syria, and 12 local governors in Iraq and Syria. Beneath the leaders are councils on finance, leadership, military matters, legal matters—including decisions on executions—foreign fighters' assistance, security, intelligence and media. In addition, a Shura council has the task of ensuring that all decisions made by the governors and councils comply with the group's interpretation of sharia.[129]
The Wall Street Journal estimated in September 2014 that eight million Iraqis and Syrians live in areas controlled by ISIL.[130] Ar-Raqqah in Syria is the de facto headquarters, and is said to be a test case of ISIL governance.[131] As of September 2014, governance in Ar-Raqqah has been under the total control of ISIL where it has rebuilt the structure of modern government in less than a year. Former government workers from the Assad regime maintain their jobs after pledging allegiance to ISIL. Institutions, restored and restructured, are providing services. The Ar-Raqqah dam continues to provide electricity and water. Foreign expertise supplements Syrian officials in running civilian institutions. Only the police and soldiers are ISIL fighters, who receive confiscated lodging previously owned by non-Sunnis and others who fled. Welfare services are provided, price controls established, and taxes imposed on the wealthy. ISIL runs a soft power program in the areas under its control in Iraq and Syria, which includes social services, religious lectures and da'wah—proselytizing—to local populations. It also performs public services such as repairing roads and maintaining the electricity supply.[132]
British security expert Frank Gardner has concluded that ISIL's prospects of maintaining control and rule are greater in 2014 than they were in 2006. Despite being as brutal as before, ISIL has become "well entrenched" among the population and is not likely to be dislodged by ineffective Syrian or Iraqi forces. It has replaced corrupt governance with functioning locally controlled authorities, services have been restored and there are adequate supplies of water and oil. With Western-backed intervention being unlikely, the group will "continue to hold their ground" and rule an area "the size of Pennsylvania for the foreseeable future", he said.[133][134] Further solidifying ISIL rule is the control of wheat production, which is roughly 40% of Iraq's production. ISIL has maintained food production, crucial to governance and popular support.[135]
Ideology and beliefs
ISIL is a Sunni extremist group. It follows an extreme interpretation of Islam, promotes religious violence, and regards those who do not agree with its interpretations as infidels or apostates—see takfirism.[136] ISIL's philosophy is well represented by the symbolism in the Black Standard variant of the legendary battle flag of Muhammad that it has adopted. The flag shows the seal of the Muhammad within a white circle, with the phrase above it, "There is no God but Allah".[137] Such symbolism has been said to point to ISIL's belief that it represents the restoration of the caliphate of early Islam, with all of the political, religious and eschatological ramifications that this would imply.[138]
According to some observers, ISIL emerged from the ideology of the Muslim Brotherhood, the first post-Ottoman Islamist group dating back to the late 1920s in Egypt.[139] It adheres to global jihadist principles and follows the hard-line ideology of al-Qaeda and many other modern-day jihadist groups.[136][140]
However, other sources trace the group's roots not to the Islamism of the Muslim Brotherhood and the more mainstream jihadism of al-Qaeda, but to Wahhabism.The New York Times wrote:
Reflecting the ideology of modern Wahhabism, which aims to return to the early days of Islam, ISIL rejects all innovations in the religion, which it believes corrupt its original spirit. It condemns later caliphates and the Ottoman Empire for deviating from what it calls pure Islam,[142] and seeks to revive the original Wahhabi project of the restoration of the caliphate governed by strict Salafist doctrine. Following Wahhabi tradition, ISIL condemns the followers of secular law as disbelievers, putting the current Saudi regime in that category.[143]
Salafists such as ISIL believe that only a legitimate authority can undertake the leadership of jihad, and that the first priority over other areas of combat, such as fighting non-Muslim countries, is the purification of Islamic society. For example, when it comes to the Israeli–Palestinian conflict, since ISIL regards the Palestinian Sunni group Hamas as apostates who have no legitimate authority to lead jihad, it regards fighting Hamas as the first step toward confrontation with Israel.[141][144]
Theological objections
According to The New York Times, "All of the most influential jihadist theorists are criticizing the Islamic State as deviant, calling its self-proclaimed caliphate null and void" and have denounced it for its beheading of journalists and aid workers.[141] ISIL is widely denounced by a broad range of Islamic clerics, including al-Qaeda-oriented and Saudi clerics.[141][145]
Sunni critics, including Salafi and jihadist muftis such as Adnan al-Aroor and Abu Basir al-Tartusi, say that ISIL and related terrorist groups are not Sunnis, but modern-day Khawarij—Muslims who have stepped outside the mainstream of Islam—serving an imperial anti-Islamic agenda.[146][147][148][149] Other critics of ISIL's brand of Sunni Islam include Salafists who previously publicly supported jihadist groups such as al-Qaeda, for example the Saudi government official Saleh Al-Fawzan, known for his extremist views, who claims that ISIL is a creation of "Zionists, Crusaders and Safavids", and the Jordanian-Palestinian writer Abu Muhammad al-Maqdisi, the former spiritual mentor to Abu Musab al-Zarqawi, who was released from prison in Jordan in June 2014 and accuses ISIL of driving a wedge between Muslims.[149]
Designation as a terrorist organization
Main articles: List of designated terrorist organizations and Terrorism
| Entity | Date | Authority | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multinational Organizations | |||
| 18 October 2004 | United Nations Security Council | [150][151] | |
| 2004 | EU Council (via adoption of UN al-Qaida Sanctions List) | [152] | |
| Nations | |||
| March 2001 (as part of al-Qaeda) 20 June 2014 (after separation from al‑Qaeda) | Home Secretary of the Home Office | [153] | |
| 17 December 2004 | United States Department of State | [154] | |
| 2 March 2005 | Attorney-General for Australia | [155] | |
| 20 August 2012 | Parliament of Canada | [156] | |
| 30 October 2013 | Grand National Assembly of Turkey | [157][158] | |
| 7 March 2014 | Royal decree of the King of Saudi Arabia | [159] | |
| 1 August 2014 | National Counter-terrorism Agency BNPT (id) | [160] | |
| 20 August 2014 | UAE Cabinet | [161] | |
| 30 November 2014 | The Cairo Court for Urgent Matters | [162][163] | |
| 16 December 2014 | Ministry of Home Affairs | [164][165] | |
The United Nations Security Council in its Resolution 1267 (1999) described Osama bin Laden and his al-Qaeda associates as operators of a network of terrorist training camps.[166] The UN's Al-Qaida Sanctions Committee first listed ISIL in its Sanctions List under the name "Al-Qaida in Iraq" on 18 October 2004, as an entity/group associated with al-Qaeda. On 2 June 2014, the group was added to its listing under the name "Islamic State in Iraq and the Levant". The European Union adopted the UN Sanctions List in 2002.[152]
Many world leaders and government spokespeople have called ISIL a terrorist group, without their countries having formally designated it as such. Media sources worldwide have also called ISIL a terrorist organization.[167][168][169][170][171]
Human rights abuse and war crime findings
In July 2014, the BBC reported the United Nations' chief investigator as stating: "Fighters from the Islamic State in Iraq and the Levant (Isis) may be added to a list of war crimes suspects in Syria."[172] By June 2014, according to United Nations reports, ISIL had killed hundreds of prisoners of war[173] and over 1,000 civilians.[174][175][176] In August 2014, the UN accused ISIL of committing "mass atrocities" and war crimes,[177][178] including the mass killing of up to 250 Syrian Armysoldiers near Tabqa Air base.[173] Other known killing of military prisoners took place in Camp Speicher (1,095–1,700 Iraqi soldiers shot and "thousands" more "missing")[179][180] and the Shaer gas field (200 Syrian soldiers shot).[181]
In early September 2014, the United Nations Human Rights Council agreed to send a team to Iraq and Syria to investigate the abuses and killings being carried out by the ISIL on "an unimaginable scale". Prince Zeid bin Ra'ad, the newly appointed UN High Commissioner for Human Rights, urged world leaders to step in to protect women and children suffering at the hands of ISIL militants, who he said were trying to create a "house of blood". He appealed to the international community to concentrate its efforts on ending the conflict in Iraq and Syria.[182]
In November 2014, the UN Commission of Inquiry on Syria said that ISIL was committing crimes against humanity.[183][184] A report by Human Rights Watch in November 2014 accused ISIL groups in control of Derna, Libya of war crimes and human rights abuses and of terrorizing residents. Human Rights Watch documented three apparent summary executions and at least ten public floggings by the Islamic Youth Shura Council, which joined ISIL in November. It also documented the beheading of three Derna residents and dozens of seemingly politically-motivated assassinations of judges, public officials, members of the security forces and others. Sarah Leah Watson, Director of HRW Middle East and North Africa, said: "Commanders should understand that they may face domestic or international prosecution for the grave rights abuses their forces are committing."[185]
Speaking of ISIL's methods, the United Nations Commission on Human Rights has stated that the group "seeks to subjugate civilians under its control and dominate every aspect of their lives through terror, indoctrination, and the provision of services to those who obey".[186]
Religious and minority group persecution
ISIL compels people in the areas that it controls to declare Islamic creed and live according to its interpretation of Sunni Islam and sharia law.[167][187] There have been many reports of the group's use of death threats, torture and mutilation to compel conversion to Islam,[167][187] and of clerics being killed for refusal to pledge allegiance to the Islamic State.[188] ISIL directs violence against Shia Muslims, indigenous Assyrian, Chaldean, Syriac and Armenian Christians, Yazidis, Druze,Shabaks and Mandeans in particular.[189]
Amnesty International has held ISIL responsible for the ethnic cleansing of ethnic and religious minority groups in northern Iraq on a "historic scale". In a special report released on 2 September 2014, it describes how ISIL has "systematically targeted non-Arab and non-Sunni Muslim communities, killing or abducting hundreds, possibly thousands, and forcing more than 830,000 others to flee the areas it has captured since 10 June 2014". Among these people are Assyrian Christians,Turkmen Shia, Shabak Shia, Yazidis, Kaka'i and Sabean Mandeans, who have lived together for centuries in Nineveh province, large parts of which are now under ISIL's control.[190][191]
Among the known killings of religious and minority group civilians carried out by ISIL are those in the villages and towns of Quiniyeh (70–90 Yazidis killed), Hardan (60 Yazidis killed), Sinjar (200–500 Yazidis killed), Ramadi Jabal (60–70 Yazidis killed), Dhola (50 Yazidis killed), Khana Sor (100 Yazidis killed), Hardan (250–300 Yazidis killed), al-Shimal (dozens of Yazidis killed), Khocho (400 Yazidis killed and 1,000 abducted), Jadala (14 Yadizis killed)[192] and Beshir (700 Shia Turkmen killed),[193] and others committed near Mosul (670 Shia inmates of the Badush prison killed),[193] and in Tal Afar prison, Iraq (200 Yazidis killed for refusing conversion).[192] The UN estimated that 5,000 Yazidis were killed by ISIL during the takeover of parts of northern Iraq in August 2014.[194] In late May 2014, 150 Kurdish boys from Kobani aged 14–16 were abducted and subjected to torture and abuse, according to Human Rights Watch.[195] In the Syrian towns of Ghraneij,Abu Haman and Kashkiyeh 700 members of the Sunni Al-Shaitat tribe were killed for attempting an uprising against ISIL control.[196][197] The UN reported that in June 2014 ISIL had killed a number of Sunni Islamic clerics who refused to pledge allegiance to it.[188]
Christians living in areas under ISIL control who want to remain in the "caliphate" face three options: converting to Islam, paying a religious levy—jizya—or death. "We offer them three choices: Islam; the dhimma contract – involving payment of jizya; if they refuse this they will have nothing but the sword", ISIL said.[198] ISIL had already set similar rules for Christians in Ar-Raqqah, once one of Syria's more liberal cities.[199][200]
Treatment of civilians
During the Iraqi conflict in 2014, ISIL released dozens of videos showing its ill treatment of civilians, many of whom had apparently been targeted on the basis of their religion or ethnicity. Navi Pillay, UN High Commissioner for Human Rights, warned of war crimes being committed in the Iraqi war zone, and disclosed a UN report of ISIL militants murdering Iraqi Army soldiers and 17 civilians in a single street in Mosul. The UN reported that in the 17 days from 5 to 22 June, ISIL killed more than 1,000 Iraqi civilians and injured more than 1,000.[174][175][176] After ISIL released photographs of its fighters shooting scores of young men, the UN declared that cold-blooded "executions" by militants in northern Iraq almost certainly amounted to war crimes.[201]
ISIL's advance in Iraq in mid-2014 was accompanied by continuing violence in Syria. On 29 May, ISIL raided a village in Syria and at least 15 civilians were killed, including, according to Human Rights Watch, at least six children.[202] A hospital in the area confirmed that it had received 15 bodies on the same day.[203] TheSyrian Observatory for Human Rights reported that on 1 June, a 102-year-old man was killed along with his whole family in a village in Hama province.[204]
In Mosul, ISIL has implemented a sharia school curriculum which bans the teaching of art, music, national history, literature and Christianity. Although Charles Darwin's theory of evolution has never been taught in Iraqi schools, the subject has been banned from the school curriculum. Patriotic songs have been declared blasphemous, and orders have been given to remove certain pictures from school textbooks.[205][206][207][208] Iraqi parents have largely boycotted schools in which the new curriculum has been introduced.[209]
After capturing cities in Iraq, ISIL issued guidelines on how to wear clothes and veils. ISIL warned women in the city of Mosul to wear full-face veils or face severe punishment.[210] A cleric told Reuters in Mosul that ISIL gunmen had ordered him to read out the warning in his mosque when worshippers gathered. ISIL ordered the faces of both male and female mannequins to be covered, in an order which also banned the use of naked mannequins.[211] In Ar-Raqqah the group uses its two battalions of female fighters in the city to enforce compliance by women with its strict laws on individual conduct.[212]
ISIL released 16 notes labeled "Contract of the City", a set of rules aimed at civilians in Nineveh. One rule stipulated that women should stay at home and not go outside unless necessary. Another rule said that stealing would be punished by amputation.[132][213] In addition to banning the sale and use of alcohol—which is customary in Muslim culture—ISIL has banned the sale and use of cigarettes and hookah pipes. It has also banned "music and songs in cars, at parties, in shops and in public, as well as photographs of people in shop windows".[214]
According to The Economist, dissidents in the ISIL capital of Ar-Raqqah report that "all 12 of the judges who now run its court system ... are Saudis". Saudi practices also followed by the group include the establishment of religious police to root out "vice" and enforce attendance at salat prayers, the widespread use of capital punishment, and the destruction of Christian churches and non-Sunni mosques or their conversion to other uses.[215]
Child soldiers
ISIL has recruited Iraqi children as young as nine to its ranks, who can be seen with masks on their faces and guns in their hands patrolling the streets of Mosul and even making arrests.[216] According to a report by the magazine Foreign Policy, children as young as six are recruited or kidnapped and sent to military and religious training camps, where they practise beheading with dolls and are indoctrinated with the religious views of ISIL. Children are used as human shields on front lines and to provide blood transfusions for Islamic State soldiers, according to Shelly Whitman of the Roméo Dallaire Child Soldiers Initiative. The second instalment of a VICE News documentary about ISIL focused on how the group is specifically grooming children for the future. A spokesman told VICE News that those under the age of 15 go to sharia camp to learn about religion, while those older than 16 can go to military training camp. Children are also used for propaganda. According to a UN report, "In mid-August, ISIL entered a cancer hospital in Mosul, forced at least two sick children to hold the ISIL flag and posted the pictures on the internet." Misty Buswell, a Save the Children representative working with refugees in Jordan, said, "It's not an exaggeration to say we could lose a whole generation of children to trauma."[217]
Sexual violence and slavery
| This section may require copy-editing. (December 2014) |
Main articles: Sexual violence in the Iraqi insurgency and Slavery in 21st century Islamism
See also: Islamic views on slavery, Ma malakat aymanukum, Slavery in 21st century Islamism and Wartime sexual violence
There are many allegations of sexual abuse and enslavement of Iraqi women and girls, predominantly from the minority Christian and Yazidi communities.[218]According to one report, ISIL's capture of Iraqi cities in June 2014 was accompanied by an upsurge in crimes against women, including kidnap and rape.[219][220][221]The Guardian reported that ISIL's extremist agenda extended to women's bodies and that women living under their control were being captured and raped.[222]Fighters are told that they are free to have sex and rape non-Muslim captive women.[223] Hannaa Edwar, a leading women’s rights advocate in Baghdad who runs anNGO called Iraqi Al-Amal Association (IAA),[224] said that none of her contacts in Mosul were able to confirm any cases of rape.[225] However, another Baghdad-based women's rights activist, Basma al-Khateeb, said that a culture of violence existed in Iraq against women generally and felt sure that sexual violence against women was happening in Mosul involving not only ISIL but all armed groups.[225] During a meeting with Nouri al-Maliki, British Foreign Minister William Hague said with regard to ISIL: "Anyone glorifying, supporting or joining it should understand that they would be assisting a group responsible for kidnapping, torture, executions, rape and many other hideous crimes".[226] According to Martin Williams in The Citizen, some hard-line Salafists apparently regard extramarital sex with multiple partners as a legitimate form of holy war and it is "difficult to reconcile this with a religion where some adherents insist that women must be covered from head to toe, with only a narrow slit for the eyes".[227]
Haleh Esfandiari from the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars has highlighted the abuse of local women by ISIL militants after they have captured an area. "They usually take the older women to a makeshift slave market and try to sell them. The younger girls ... are raped or married off to fighters", she said, adding, "It's based on temporary marriages, and once these fighters have had sex with these young girls, they just pass them on to other fighters."[228] Speaking ofYazidi women captured by ISIL, Nazand Begikhani said, "These women have been treated like cattle... They have been subjected to physical and sexual violence, including systematic rape and sex slavery. They've been exposed in markets in Mosul and in Raqqa, Syria, carrying price tags."[229] Yazidi girls in Iraq allegedlyraped by ISIL fighters have committed suicide by jumping to their death from Mount Sinjar, as described in a witness statement.[230]
A United Nations report issued on 2 October 2014, based on 500 interviews with witnesses, said that ISIL took 450–500 women and girls to Iraq's Nineveh region in August, where "150 unmarried girls and women, predominantly from the Yazidi and Christian communities, were reportedly transported to Syria, either to be given to ISIL fighters as a reward or to be sold as sex slaves".[218] In mid-October, the UN confirmed that 5,000–7,000 Yazidi women and children had been abducted by ISIL and sold into slavery.[231][232] In November 2014 The New York Times reported on the accounts given by five who escaped ISIL of their captivity and abuse.[233] In its digital magazine Dabiq, ISIL explicitly claimed religious justification for enslaving Yazidi women.[234][235][236][237][238][239] According to The Wall Street Journal, ISIL appeals to apocalyptic beliefs and claims "justification by a Hadith that they interpret as portraying the revival of slavery as a precursor to the end of the world".[240]
In late 2014 ISIL released a pamphlet on the treatment of female slaves.According to the latest report in December 2014 by USA Today , ISIS distributed pamphlets stating that its fighters are allowed to have sex with adolescent girls, and that it is also acceptable to beat and trade them.[241] On the contrary, it says it is permissible to beat a slave so long as it's a form of disciplinary beating and also that it is forbidden for fighters to hit the female captives in the face. However, the pamphlets says a woman can't be sold if she becomes impregnated by her owner. In addition to that some pamphlets explicitly cite the Quran to back up its claims. In answering whether it's OK to have sex with a captive, the pamphlet states, "It is permissible to have sexual intercourse with the female captive. Allah the almighty said: "(Successful are the believers) who guard their chastity, except to their wives or (the captives and slaves) that their right hands possess, for then they are free from blame" (Koran 23:5-6).As of mid December 2014 ISIS released 'abhorrent' sex slaves pamphlet with 27 tips for militants on taking, punishing and raping female captives, many people living in that part were taken aback after they read the pamphlets and stated that they never expected this move from the ISIS government[242][243][244][245][246][247][248]
In December 2014 the Iraqi Ministry of Human Rights announced that ISIL had killed over 150 women and girls in Fallujah who refused to participate in sexual jihad.[249][250]
Attacks on members of the press
The Committee to Protect Journalists states: "Without a free press, few other human rights are attainable."[251] ISIL has tortured and murdered local journalists,[252][253] creating what Reporters Without Borders calls "news blackholes" in areas controlled by ISIL. ISIL fighters have reportedly been given written directions to kill or capture journalists.[254]
In December 2013, two suicide bombers stormed the headaquarters of TV station Salaheddin and killed five journalists, after accusing the station of "distorting the image of Iraq's Sunni community". Reporters Without Borders reported that on 7 September 2014, ISIL seized and on 11 October publicly beheaded Raad al-Azzawi, a TV Salaheddin cameraman from the village of Samra, east of Tikrit.[255] As of October 2014, according to the Journalistic Freedoms Observatory, ISIL is holding nine journalists and has nine others under close observation in Mosul and Salahuddin province.[254]
During 2013 and part of 2014, an ISIL unit nicknamed the Beatles acquired and held 12 Western journalists hostage, along with aid workers and other foreign hostages, totaling 23 or 24 known hostages. A Polish journalist Marcin Suder was captured in July 2013 but escaped four months later.[256] The unit executed American journalists James Foley and Steven Sotloff and released beheading videos. Eight of the other journalists were released for ransom: Danish journalist Daniel Rye Ottosen, French journalists Didier François, Edouard Elias, Nicolas Hénin, and Pierre Torres, and Spanish journalists Marc Marginedas, Javier Espinosa, and Ricardo García Vilanova. The unit continues to hold hostage British journalist John Cantlie and a female aid worker.[257]
Beheadings and mass executions
Main article: 2014 ISIL beheading incidents
An unknown number of Syrians and Iraqis, several Lebanese soldiers, at least ten Kurds, two American journalists, one American and two British aid workers, and three Libyans have been beheaded by the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant. ISIL uses beheadings to intimidate local populations and has released a series of propaganda videos aimed at Western countries. They also engage in public and mass executions, sometimes forcing prisoners to dig their own graves before shooting lines of prisoners and pushing them in.[258][259] ISIL was reported to have beheaded about 100 foreign fighters as deserters who tried to leave Raqqa.[260]
Destruction of cultural and religious heritage
UNESCO's Director-General Irina Bokova has warned that ISIL is destroying Iraq's cultural heritage, in what she has termed "cultural cleansing". "We don't have time to lose because extremists are trying to erase the identity, because they know that if there is no identity, there is no memory, there is no history", she said. Referring to the ancient cultures of Christians, Yazidis and other minorities, she said, “This is a way to destroy identity. You deprive them of their culture, you deprive them of their history, their heritage, and that is why it goes hand in hand with genocide. Along with the physical persecution they want to eliminate – to delete – the memory of these different cultures. ... we think this is appalling, and this is not acceptable." [261] Saad Eskander, head of Iraq’s National Archives said, “For the first time you have cultural cleansing... For the Yazidis, religion is oral, nothing is written. By destroying their places of worship … you are killing cultural memory. It is the same with the Christians – it really is a threat beyond belief.”[262]
In order to finance its activities, ISIL is stealing artifacts from Syria and Iraq and sending them to Europe to be sold. It is estimated that ISIL raises US$200 million a year from cultural looting. UNESCO has asked for United Nations Security Council controls on the sale of antiquities, similar to those imposed after the 2003 Iraq War. UNESCO is working with Interpol, national customs authorities, museums, and major auction houses in attempts to prevent looted items being sold.[262] ISIL occupied Mosul Museum, the second most important museum in Iraq, as it was about to reopen after years of rebuilding following the Iraq War, saying that the statues were against Islam and threatening to destroy the museum's contents.[263][264]
ISIL considers worshipping at graves tantamount to idolatry, and seeks to purify the community of unbelievers. It has used bulldozers to crush buildings and archeological sites.[264] Bernard Haykel has described Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi's creed as "a kind of untamed Wahhabism", saying, "For Al Qaeda, violence is a means to an ends; for ISIS, it is an end in itself".[141] The destruction by ISIL in July 2014 of the tomb and shrine of the prophet Yunus—Jonah in Christianity—the 13th century mosque of Imam Yahya Abu al-Qassimin, the 14th century shrine of prophet Jerjis—St George to Christians—and the attempted destruction of the Hadbaminaret at the 12th century Great Mosque of Al-Nuri have been described as "an unchecked outburst of extreme Wahhabism".[265] "There were explosions that destroyed buildings dating back to the Assyrian era", said National Museum of Iraq director Qais Rashid, referring to the destruction of the shrine of Yunus. He cited another case where "Daesh (ISIL) gathered over 1,500 manuscripts from convents and other holy places and burnt all of them in the middle of the city square".[266]
There is also the fear that warfare waged on any side will harm cultural heritage. “The worst thing about wars is that they do not distinguish between the past and the future", Mosul calligrapher and conservationist Abdallah Ismail told a local correspondent for the German-funded publication Niqash.org. He suggested that ISIL was “taking the pulse” of the local population to see how it would react to their appetite for destruction. Philippe Lalliot, France's ambassador to UNESCO gave this perspective: "When people die in their tens of thousands, must we be concerned about cultural cleansing? Yes, definitely yes ... It's because culture is a powerful incentive for dialogue that the most extreme and the most fanatical groups strive to annihilate it."[266] According to the London Charter and several Hague Conventions, the destruction of historical sites and places of worship is a war crime.[267]
Organ trafficking
According to media reports, ISIL has established a system for harvesting and selling human organs from fighters, captives and hostages, including minority children in Mosul and other areas. They are using imported teams of doctors who are not allowed to interact with local medical staff.[268][269][270][271]
Criticism
Islamic criticism
ISIL has been at the receiving end of severe criticism from other Muslims, especially religious scholars and theologians. In late August 2014, the Grand Mufti of Saudi Arabia, Abdul-Aziz ibn Abdullah Al ash-Sheikh, condemned the Islamic State and al-Qaeda saying, “Extremist and militant ideas and terrorism which spread decay on Earth, destroying human civilisation, are not in any way part of Islam, but are enemy number one of Islam, and Muslims are their first victims”.[272] In late September 2014, 126 Sunni imams and Islamic scholars—primarily Sufi[273]—from around the Muslim world signed an open letter to the Islamic State's leader Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, explicitly rejecting and refuting his group's interpretations of Islamic scriptures, the Qur'an and hadith, used by it to justify its actions.[274][275] "[You] have misinterpreted Islam into a religion of harshness, brutality, torture and murder ... this is a great wrong and an offence to Islam, to Muslims and to the entire world", the letter states.[276] It rebukes the Islamic State for its killing of prisoners, describing the killings as "heinous war crimes" and its persecution of the Yazidis of Iraq as "abominable". Referring to the "self-described 'Islamic State'", the letter censures the group for carrying out killings and acts of brutality under the guise of jihad—holy struggle—saying that its "sacrifice" without legitimate cause, goals and intention "is not jihad at all, but rather, warmongering and criminality".[276][277] It also accuses the group of instigating fitna—sedition—by instituting slavery under its rule in contravention of the anti-slavery consensus of the Islamic scholarly community.[276] Other scholars have described the group as not Sunnis, but Khawarij.[278]
The group's declaration of a caliphate has been criticized and its legitimacy disputed by Middle Eastern governments, other jihadist groups,[279] and Sunni Muslim theologians and historians. Qatar-based TV broadcaster and theologian Yusuf al-Qaradawi stated: "[The] declaration issued by the Islamic State is void under sharia and has dangerous consequences for the Sunnis in Iraq and for the revolt in Syria", adding that the title of caliph can "only be given by the entire Muslim nation", not by a single group.[280]
Two days after the beheading of Hervé Gourdel, hundreds of Muslims gathered in the Grand Mosque of Paris to show solidarity against the beheading. The protest was led by the leader of the French Council of the Muslim Faith, Dalil Boubakeur, and was joined by thousands of other Muslims around the country under the slogan "Not in my name".[281][282]French president François Hollande said Gourdel's beheading was "cowardly" and "cruel", and confirmed that airstrikes would continue against ISIL in Iraq. Hollande also called for three days of national mourning, with flags flown at half-mast throughout the country and said that security would be increased throughout Paris.[281]
International criticism
The group has attracted widespread criticism internationally for its extremism, from governments and international bodies such as the United Nations and Amnesty International. On 24 September 2014, United Nations Secretary-General Ban Ki-Moon stated: "As Muslim leaders around the world have said, groups like ISIL – or Da’ish -- have nothing to do with Islam, and they certainly do not represent a state. They should more fittingly be called the "Un-Islamic Non-State"."[283] The group was described as a cult in a Huffington Post column by notable cult authority Steven Hassan.[284]
Criticism of the name "Islamic State" and "caliphate" declaration
The declaration of a new caliphate in June 2014 and the name "Islamic State" have been criticized and ridiculed by Muslim scholars and rival Islamists inside and outside the territory it controls.[285][286][287][288] In a speech in September 2014, President Obama said that, ISIL is not “Islamic” on the basis that no religion condones the killing of innocents and that no government recognises the group as a state,[289] and many object to using the name "Islamic State" owing to the far-reaching religious and political claims to authority which that name implies. The United Nations Security Council, the United States, Canada, Turkey, Australia, Russia, the United Kingdom[290][291][292][293][294][295][296] and other countries generally call the group "ISIL", while much of the Arab world uses the Arabic acronym "Dāʻish". France's Foreign Minister Laurent Fabius said "This is a terrorist group and not a state. I do not recommend using the term Islamic State because it blurs the lines between Islam, Muslims, and Islamists. The Arabs call it 'Daesh' and I will be calling them the 'Daesh cutthroats.'"[297] Retired general John Allen, the US envoy to coordinate the coalition, US Lieutenant General James Terry, head of operations against the group, and Secretary of State John Kerry have all shifted toward the term DAESH by December 2014.[298]
In late August 2014, a leading Islamic educational institution, Dar al-Ifta al-Misriyyah in Egypt, advised Muslims to stop calling the group "Islamic State" and instead refer to it as "Al-Qaeda Separatists in Iraq and Syria" or "QSIS", because of the militant group's "un-Islamic character".[299][300] When addressing the United Nations Security Council in September 2014, Australian Prime Minister Tony Abbott summarized the widespread objections to the name "Islamic State" thus: "To use this term [Islamic State] is to dignify a death cult; a death cult that, in declaring itself a caliphate, has declared war on the world".[301] The group is very sensitive about its name. "They will cut your tongue out even if you call them Isis – you have to say 'Islamic State'", said a woman in ISIL-controlled Mosul.[302]
In mid-October 2014, representatives of the Islamic Society of Britain, the Association of British Muslims and the UK's Association of Muslim Lawyers proposed that "'Un-Islamic State' (UIS) could be an accurate and fair alternative name to describe this group and its agenda", further stating, "We need to work together and make sure that these fanatics don't get the propaganda that they feed off."[303][304] The "Islamic State" is mocked on social media websites such as Twitter and YouTube, with the use of hashtags, mock recruiting ads, fake news articles and YouTube videos.[305] One parody, by a Palestinian TV satire show, portrays ISIL as "buffoon-like hypocrites", and has had more than half a million views on YouTube.[305][306]
Analysis
See also: History of Iraq and History of Syria
By 2014, ISIL was increasingly being viewed as a militia rather than as a terrorist group.[307] As major Iraqi cities fell to ISIL in June 2014, Jessica Lewis, a former US army intelligence officer at the Institute for the Study of War, described ISIL as "not a terrorism problem anymore", but rather "an army on the move in Iraq and Syria, and they are taking terrain. They have shadow governments in and around Baghdad, and they have an aspirational goal to govern. I don't know whether they want to control Baghdad, or if they want to destroy the functions of the Iraqi state, but either way the outcome will be disastrous for Iraq." Lewis has called ISIL "an advanced military leadership". She said, "They have incredible command and control and they have a sophisticated reporting mechanism from the field that can relay tactics and directives up and down the line. They are well-financed, and they have big sources of manpower, not just the foreign fighters, but also prisoner escapees."[307]
While officials[which?] fear that ISIL may either inspire attacks in the United States by sympathizers or by those returning after joining ISIL, US intelligence agencies find there is no immediate threat or specific plots. US Defense Secretary Chuck Hagel sees an "imminent threat to every interest we have", but former top counterterrorism adviser Daniel Benjamin has derided such alarmist talk as a "farce" that panics the public.[308]
Some news commentators, such as international newspaper columnist Gwynne Dyer,[309] and samples of public opinion, such as surveys by NPR,[310] have advocated a strong but measured response to ISIL's recent provocative acts.
Conspiracy theories in the Arab world
Conspiracy theorists in the Arab world have advanced rumors that the US is secretly behind the existence and emboldening of ISIL, as part of an attempt to further destabilize the Middle East. After such rumors became widespread, the US embassy in Lebanon issued an official statement denying the allegations, calling them a complete fabrication.[311] Others[which?] are convinced that ISIL leader Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi is an Israeli Mossad agent and actor called Simon Elliot. The rumors claim that NSA documents leaked by Edward Snowden reveal this connection. Snowden's lawyer has called the story "a hoax."[312][313][314]
Countries and groups at war with ISIL
ISIL's expanding claims to territory have brought it into armed conflict with many governments, militias and other armed groups. International rejection of ISIL as a terrorist entity and rejection of its claim to even exist have placed it in conflict with countries around the world.
Opposition within Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Egypt and Libya
| Iraqi Insurgency | Syrian Civil War | Other Conflicts |
|---|---|---|
Iraq-based opponents
|
|
Lebanon-based opponents
Egypt-based opponents
Libya-based opponents
Abu Salim Martyrs Brigade (Libyan rebel group)[332]
|
Global Coalition to Counter the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant
The Global Coalition to Counter the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL or Daesh), also referred to as the Counter-ISIL Coalition or Counter-DAESH Coalition,[333] is a US-led group of nations and non-state actors that have committed to "work together under a common, multifaceted, and long-term strategy to degrade and defeat ISIL/Daesh". According to a joint statement issued by 59 national governments and the European Union, participants in the Counter-ISIL Coalition are focused on multiple lines of effort:[334]
- Supporting military operations, capacity building, and training;
- Stopping the flow of foreign terrorist fighters;
- Cutting off ISIL/Daesh’s access to financing and funding;
- Addressing associated humanitarian relief and crises; and
- Exposing ISIL/Daesh’s true nature (ideological delegitimization).
Operation Inherent Resolve is the operational name given by the US to military operations against ISIL and Syrian al-Qaeda affiliates. Combined Joint Task Force - Operation Inherent Resolve is coordinating the military portion of the response.
The following multi-national organizations are part of the Counter-ISIL Coalition:[334]
 European Union – declared to be part, most members are participating;[334]
European Union – declared to be part, most members are participating;[334]
 NATO – all 27 members are taking part;
NATO – all 27 members are taking part;
 Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf or GCC – all six current members and the two pending members, Jordan and Morocco, are taking part.
Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf or GCC – all six current members and the two pending members, Jordan and Morocco, are taking part.
| Military operations in or over Iraq and/or Syria airstrikes, air support, and ground forces performing training | Supplying military equipment to opposition forces within Iraq and/or Syria in cooperation with EU/NATO/partners | Humanitarian and other contributions to identified coalition objectives |
|---|---|---|
Other:
Part of the Counter-ISIL Coalition engaged in anti-ISIL military operations within their own borders[334]
Note: Listed countries in this box may also be supplying military and humanitarian aid, and contributing to group objectives in other ways.
|
Other:
Note: These countries may also be supplying humanitarian aid and contributing to group objectives in other ways.
|
Other
|
Other state opponents
Other non-state opponents
 al-Nusra Front[364]—with localized truces and cooperation at times
al-Nusra Front[364]—with localized truces and cooperation at times
Supporters
Groups with expressions of support
Memberships of these groups have declared support for ISIL, either fully or in part.
 Boko Haram (Nigeria and surrounding countries)[366]
Boko Haram (Nigeria and surrounding countries)[366] Bangsamoro Islamic Freedom Fighters (Philippines)[367]
Bangsamoro Islamic Freedom Fighters (Philippines)[367] Jemaah Islamiyah (Southeast Asia)[368]
Jemaah Islamiyah (Southeast Asia)[368]- Ansar al-Sharia (Tunisia)[369][370]
- Ansar al-Sharia (Libya)[371][372]
 Mujahideen Shura Council in the Environs of Jerusalem (Gaza Strip)[373]
Mujahideen Shura Council in the Environs of Jerusalem (Gaza Strip)[373] Islamic Movement of Uzbekistan[374]
Islamic Movement of Uzbekistan[374] Jamaah Ansharut Tauhid (Indonesia)[375] - (pledged support to ISIL; majority of the group split off after its leader pledged allegiance to ISIL)[376][377]
Jamaah Ansharut Tauhid (Indonesia)[375] - (pledged support to ISIL; majority of the group split off after its leader pledged allegiance to ISIL)[376][377]
By mid-November 2014, the Terrorism Research and Analysis Consortium (TRAC) in Florida had identified 60 jihadist groups in 30 countries that have pledged allegiance or support to ISIL. "We at TRAC are constantly adding to the list (nearly daily)", it said. Many groups of these groups were previously affiliated with al-Qaeda, indicating a shift in global jihadist leadership toward ISIL.[378]
Turkey – allegations of support
Main article: Turkish involvement in the 2014 military intervention against ISIL § Alleged support of ISIL
Turkey has been accused of supporting or colluding with ISIL, especially by Syrian Kurds.[379][380] Turkey has also been criticized for allowing individuals from outside the region to enter its territory and join ISIL in Syria.[381][382] However, Turkey sent special forces to Iraq to train Kurdish forces in late October or early November 2014.[343]
Military and resources
Military
Main article: Military of ISIL
Estimates of the size of ISIL's military vary widely from tens of thousands up to 200,000 fighters.[11][383]
Foreign fighters in Iraq and Syria
There are thousands to tens of thousands of foreign fighters in ISIL's ranks. Estimates vary from nearly 1,000 from Chechnya, including ISIL senior commander Abu Omar al-Shishani, around 500 from France, Britain, and elsewhere in Europe,[384][385] to more than 2,000 Europeans, 100 Americans[386] and around 1,000 Turks.[387] By October 2014, there were 2,400–3,000 Tunisians[388] fighting in Iraq and Syria.
Fighters in Libya
The Shura Council of Islamic Youth and other militants in Libya were absorbed and designated the Barka Province of ISIL.[389][390] There are 800 fighters reported to be operating within Libya.
Fighters in Egypt
Ansar Bait al-Maqdis was dissolved with a large Sinai-based part of the group pledging allegiance to ISIL, which assumed the designation Province of Sinai—Wilayat Sinai—of ISIL.[389][391] They are estimated to have 1,000–2,000[26] fighters.[392]
Other areas
 Jund al-Khilafah (Algeria) - (dissolved with allegiance to and designated a province of ISIL)[24]
Jund al-Khilafah (Algeria) - (dissolved with allegiance to and designated a province of ISIL)[24]- Unidentified militants in Saudi Arabia and Yemen - designated as provinces of ISIL[24]
- Militants of the group Sons of the Call for Tawhid and Jihad (Jordan) pledging allegiance to ISIL[393]
- Militants of the group Free Sunnis of Baalbek Brigade (Lebanon) pledging allegiance to ISIL[26]
 Militants of the groups Jundallah,[394] Tehreek-e-Khilafat, and Jamaat al-Ahrar[26](Pakistan) pledging allegiance to ISIL
Militants of the groups Jundallah,[394] Tehreek-e-Khilafat, and Jamaat al-Ahrar[26](Pakistan) pledging allegiance to ISIL Militants of the group Abu Sayyaf (Philippines, Malaysia)[395] pledging allegiance to ISIL[26]
Militants of the group Abu Sayyaf (Philippines, Malaysia)[395] pledging allegiance to ISIL[26]
Conventional weapons
ISIL relies mostly on captured weapons. Major sources are Saddam Hussein's Iraqi stockpiles from the 2003-11 Iraq insurgency[396] and weapons from government and opposition forces fighting in the Syrian Civil War and during the post-US withdrawal Iraqi insurgency. The captured weapons, including armor, guns, surface-to-air missiles, and even some aircraft, enabled rapid territorial growth and facilitated the capture of additional equipment.[397]
Non-conventional weapons
The group has a long history of using truck and car bombs, suicide bombers, and IEDs, and has used chemical weapons in Iraq and Syria.. ISIL captured nuclear materials from Mosul University in July 2014, but is unlikely to be able to turn them into weapons.[398][399]
Propaganda and social media
ISIL is known for its extensive and effective use of propaganda.[400][401] It uses a version of the Muslim Black Standard flag and developed an emblem which has clear symbolic meaning in the Muslim world.[402]
In November 2006, shortly after the group's rebranding as the "Islamic State of Iraq", the group established the al-Furqan Institute for Media Production, which produces CDs, DVDs, posters, pamphlets, and web-related propaganda products.[403]ISIL's main media outlet is the I'tisaam Media Foundation,[404] which was formed in March 2013 and distributes through theGlobal Islamic Media Front (GIMF).[405]
In 2014, ISIL established the al-Hayat Media Center, which targets a Western audience and produces material in English, German, Russian and French.[406][407] Also in 2014, ISIL launched the Ajnad Media Foundation, which releases jihadist audio chants.[408] In December 2014, FBI Director James Comey stated that ISIL's "propaganda is unusually slick. They are broadcasting ... in something like 23 languages".[409]
From July 2014, al-Hayat began publishing a digital magazine called Dabiq, in a number of different languages including English. According to the magazine, its name is taken from the town of Dabiq in northern Syria, which is mentioned in a hadithabout Armageddon.[410]
ISIL's use of social media has been described by one expert as "probably more sophisticated than [that of] most US companies".[400][411] It regularly takes advantage of social media, particularly Twitter, to distribute its message by organizing hashtag campaigns, encouraging Tweets on popular hashtags, and utilizing software applications that enable ISIL propaganda to be distributed to its supporters' accounts.[412] Another comment is that "ISIS puts more emphasis on social media than other jihadi groups.... They have a very coordinated social media presence."[413] In August 2014, Twitter administrators shut down a number of accounts associated with ISIL. ISIL recreated and publicized new accounts the next day, which were also shut down by Twitter administrators.[414] The group has attempted to branch out into alternative social media sites, such as Quitter, Friendica and Diaspora; Quitter and Friendica, however, almost immediately worked to remove ISIL's presence from their sites.[415]
In a switch from its former practices, ISIL's media arm imposed a social media blackout on 27 September 2014, fearing that tweets and posts would give away military positions.[416] ISIL has also attempted to present a more "rational argument" in its series of "press release/discussions" performed by hostage/captive John Cantlieand posted on YouTube. In its most recent "Cantlie presentation", various current and former US officials were quoted, such as US President Barack Obama and former CIA station chief Michael Scheuer.[417]
Finances
In 2014, the RAND Corporation carried out a study of 200 documents—personal letters, expense reports and membership rosters—that had been captured fromIslamic State of Iraq (al-Qaeda in Iraq).[418] It found that from 2005 until 2010, outside donations amounted to only 5% of the group's operating budgets, with the rest being raised within Iraq.[418] In the time period studied, cells were required to send up to 20% of the income generated from kidnapping, extortion rackets and other activities to the next level of the group's leadership. Higher-ranking commanders would then redistribute the funds to provincial or local cells that were in difficulties or needed money to conduct attacks.[418] The records show that the Islamic State of Iraq was dependent on members from Mosul for cash, which the leadership used to provide additional funds to struggling militants in Diyala, Salahuddin and Baghdad.[418]
In mid-2014, Iraqi intelligence obtained information from an ISIL operative which revealed that the organization had assets worth US$2 billion,[419] making it the richest jihadist group in the world.[420] About three quarters of this sum is said to be represented by assets seized after the group captured Mosul in June 2014; this includes possibly up to US$429 million looted from Mosul's central bank, along with additional millions and a large quantity of gold bullion stolen from a number of other banks in Mosul.[421][422] However, doubt was later cast on whether ISIL was able to retrieve anywhere near that sum from the central bank,[423] and even on whether the bank robberies had actually occurred.[424]
Exporting oil from oilfields captured by ISIL brings in tens of millions of dollars.[133][425] One US Treasury official has estimated that ISIL earns US$1 million a day from the export of oil. Much of the oil is sold illegally in Turkey.[426] Dubai-based energy analysts have put the combined oil revenue from ISIL's Iraqi-Syrian production as high as US$3 million per day.[427] ISIL also extracts wealth through taxation and extortion.[426]
Today the majority of the group's funding comes from the production and sale of energy. It controls around 300 oil wells in Iraq alone. At its peak, it operated 350 oil wells in Iraq, but lost 45 to foreign airstrikes. It has captured 60% of Syria's total production capacity. About one fifth of its total capacity is in operation. ISIL earned US$2.5 million a day by selling 50,000–60,000 barrels of oil daily.[426][428] Foreign sales rely on a long-standing black market to export via Turkey. Many of the smugglers and corrupt Turkish border guards who helped Saddam Hussein to evade sanctions are helping ISIL to export oil and import cash.[428][429][430] Energy sales include selling electric power from captured power plants in northern Syria; some of this electricity is reportedly sold back to the Syrian government.[431]
Sales of artifacts may be the second largest source of funding for ISIL, according to an article in Newsweek. More than a third of Iraq's important sites are under ISIL's control. It looted the 9th century BC grand palace of the Assyrian king Ashurnasirpal II at Kalhu. Tablets, manuscripts and cuneiforms were sold, worth hundreds of millions of dollars. Stolen artifacts are smuggled into Turkey and Jordan. Abdulamir al-Hamdani, an archaeologist from SUNY Stony Brook, has said that ISIL is "looting... the very roots of humanity, artifacts from the oldest civilizations in the world".[428]
The group routinely practises extortion, by demanding money from truck drivers and threatening to blow up businesses, for example. Robbing banks and gold shops has been another source of income.[168]
ISIL is widely reported as receiving funding from private donors in the Gulf states,[432][433] and the governments of Iraq and Iran have repeatedly accused Saudi Arabia and Qatar of financing and supporting the group. Ahead of the conference of the US-led anti-ISIL coalition held in Paris in September 2014, France's foreign minister acknowledged that a number of countries at the table had “very probably” financed ISIL's advances.[434]
Although Iran and Iraqi Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki have accused Saudi Arabia and Qatar of funding the group,[435][436][437][438] there is reportedly no evidence that this is the case.[109][438][439][440] However, according to The Atlantic, ISIL may have been a major part of Saudi Arabian Bandar bin Sultan’s covert-ops strategy in Syria.[441]
Unregistered charity organizations are used as fronts to pass funds to ISIL. As they use aliases onFacebook's WhatsApp and Kik, the individuals and organizations are untraceable. Donations transferred to fund ISIL's operations are disguised as "humanitarian charity". Saudi Arabia has imposed a blanket ban on unauthorized donations destined for Syria as the only means of stopping such funding.[428]
Since 2012, ISIL has produced annual reports giving numerical information on its operations, somewhat in the style of corporate reports, seemingly in a bid to encourage potential donors.[400][442]
On 11 November 2014, ISIL announced that they intended to mint their own gold, silver and copper coins, based on the coinage used by the Umayyad Caliphate in the 7th Century. Following the announcement, the group began buying up gold, silver and copper in markets throughout northern and western Iraq, according to precious metal traders in the area. Members of the group also reportedly began stripping the insulation off power electrical cables in order to obtain the copper wiring.[443][444] The announcement included designs of the proposed coins, which displayed imagery including a map of the world, a sword and shield, the Al-Aqsa Mosque and a crescent moon. Economics experts, such as Professor Steven H. Hanke of Johns Hopkins University, were skeptical of the plans.[444][445] See alsoModern gold dinar.
Timeline of recent events
See also: Islamic State of Iraq § Timeline, Syrian Civil War § Course of events and Terrorist incidents in Iraq in 2014
- Index to main: 2013 events; 2014 events: January, February, March, April, May, June, July, August, September, October, November, December.
December 2014
- 15 December: The 2014 Sydney hostage crisis occurs. A café near the Martin Place was terrorized by Man Haron Monis.[446]
- 16 December: India bans ISIL, some officials fearing that the ban may impact the fate of 39 Indian construction workers who were captured by ISIL in Iraq. [447]
- 17 December: Peshmerga forces launched the Sinjar offensive from Zumar and managed to break the siege of Mount Sinjar, recapture more than 700 square kilometers of territory,[448] close in on Tal Afar, clear areas north of Mount Sinjar,[449] and push into the city of Sinjar.[450] The offensive is ongoing as of now.
- 18 December: Three rebel groups near the Golan Heights region, which had previously been aided by the United States, switched sides and pledged loyalty to ISIL.[451]
- 19 December: US General James Terry announced that the number of US airstrikes on ISIL had increased to 1,361.[452]
- 22 December: Kurdish forces claim that ISIL control of Kobanî was reduced to 30%.[453]
- 24 December: SOHR reports ISIL shot down a warplane near al-Raqqa, and ISIL supporters claim on social media, with photos, to have captured the Jordanian pilot.[454] Also, an ISIL suicide bombing in Madin killed 15 pro-government Sunni fighters and 7 Iraqi soldiers, and wounded 55.[455]



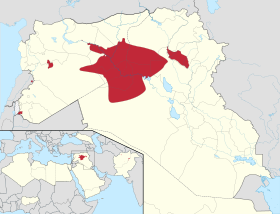








No comments:
Post a Comment